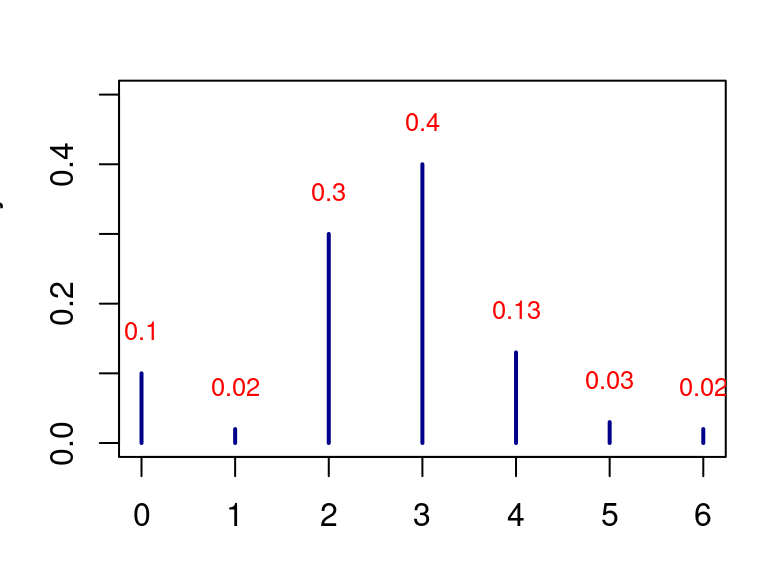
Random Variable
Discrete and Continuous Probability Distributions
Concepts
Random Variable
Are these correct?
- Discrete
- No. of people dying each day
- Number of heads in successive tosses.
- Heights of people in Bangladesh
- Continuous
- GPA of students
- Grade of students in individual subjects
- Income tax paid by people
Integration
- \(\int x^3+2x\)
- \(\int_2^3 x^2+x\)
- Relationship between integration (I) and differentiation(D).
\(f(x) \to I \to D \to f(x)\)
Test with \(f(x) = x^2\)
Probability Distribution
Example
Results of an unbiased die throw
| x | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | \(\frac 1 6\) | \(\frac 1 6\) | \(\frac 1 6\) | \(\frac 1 6\) | \(\frac 1 6\) | \(\frac 1 6\) |
Biased
| x | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | \(\frac 1 7\) | \(\frac 2 7\) | \(\frac 1 7\) | \(\frac 1 7\) | \(\frac 1 7\) | \(\frac 1 7\) |
Number of Heads in Coin Toss
A coin is tossed twice
S = {HH, HT, TH, TT}
- X = number of heads in the tosses
- What are the possible values of x?
- x = 0, 1, 2
Fill the probabilities
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| p(x) |
- N:B: X is variable & x is value
PDF vs PMF Curve
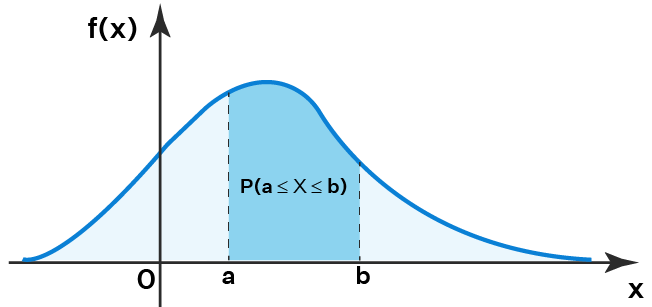
Continuous
PMF
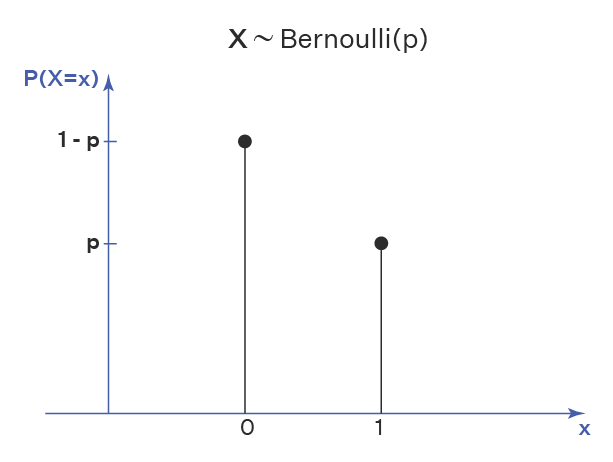
Discrete
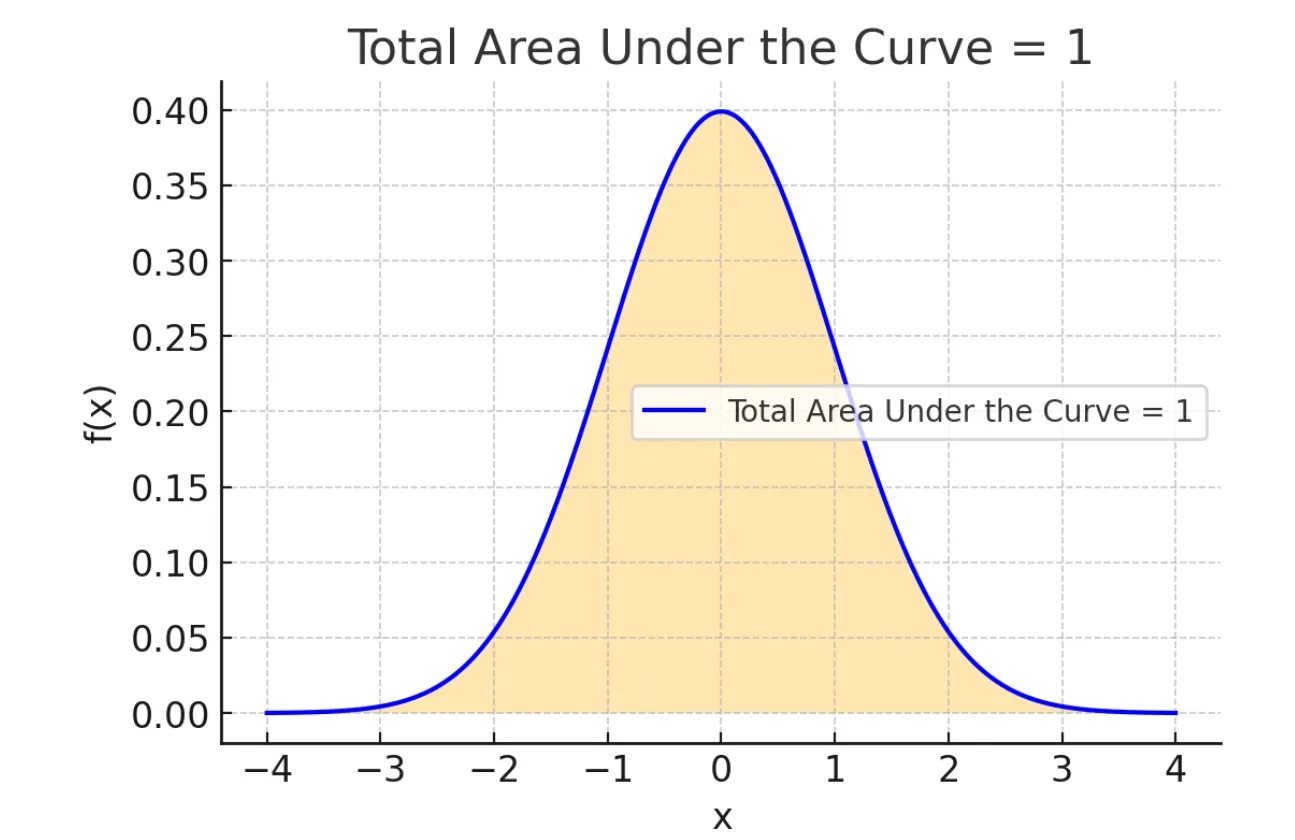
Integration and Area
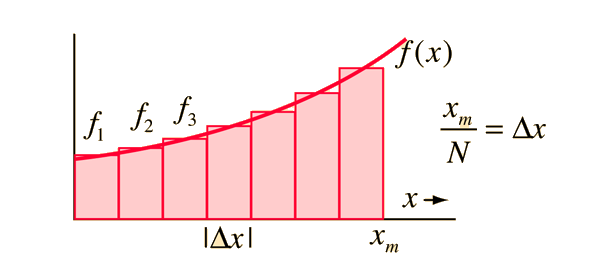 Source: hyperphysics
Source: hyperphysics
- Area = Integration = Probability (if [0,1])
- \(Area = height \times width = \int f(x) \times dx\)
PDF and PMF Conditions
PMF
- \(0 \le P(X=x) \le 1\)
- \(\sum P(x_i) = 1\)
- Thus the sum of all possible outcomes is zero
PDF and PMF Properties
Probability Density Function (continuous)
- \(\displaystyle \int_{{\, - \infty }}^{{\,\infty }}{{f\left( x \right)\,dx}} = 1\)
- \(P\left( {a \le X \le b} \right) = \int_{{\,a}}^{{\,b}}{{f\left( x \right)\,dx}}\)
- \(P(X=x)=0\) (theoretically, why?)
Probability Mass Function (discrete)
- \(\displaystyle \sum_{{\, - \infty }}^{{\,\infty }}{{f\left( x \right)\,dx}} = 1\)
- \(P_x(X) = P(X=x)\)
PMF Problem 01
\(\displaystyle P(x) = \frac{x+1}{k}; x= 1,2,3,4\)
- k = ?
- \(P(X \ge2)\)
- \(P(X \le 3)\)
- \(P(2 < X \le 5\)
PMF Problem 02
Given, \(P(x) = \frac{2x+k}{56}; x = -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3\)
Discrete or Continuous?
- k = ?
- Find probability of each value of x
- Find \(P(-2 \le x \le 2)\)
More PMF
- \(P(x) = \frac{1}{14} (a+2x); x = -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3\)
- \(P(x) = k(x-2); x = 3, 4,5,6,7,8\)
- \(P(x) = \frac{x-1}{k}; x=2,3,4,5\)
- \(P(x) = \frac{3-|4-x|}{k}; x=2,3,4,5,6\)
- \(p(x) = \frac{x+4}{30}; x=0,1,2,3,4\)
PMF problem from coin
An unbiased coin is tossed four times and the number of times the heads are obtained is denoted by x. Determine the probability mass function.
- \(S = \{HHHH, HHHT, \cdots\}\)
- \(x = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4\)
- \(P(X = 2) = \frac{4C_2}{2^4}\)
- \(P(x) = \frac{4C_X}{2^4}\)
PDF Problem 01
\(\displaystyle f(x) = kx(x-1); 1\le x \le 5\)
- Find k
- \(P(X>1)\)
- \(P(X \le 3)\)
- \(P(2 \le x < 4)\)
PDF Problem 02
\(f(x) = k(x+1); 0\lt x \lt 1\)
- \(P(X=2)=?\)
- \(k=?\)
- \(P(0.4 \lt X \lt 2)=?\)
- \(\int_{0.4}^1 f(x) + \int_{1}^2 f(x) \to 0\)
More PDF
- \(f(x) = 2x; 0 < x < 1\)
- \(f(x) = \frac{1}{30} (3+2x); 2 < x < 5\)
- \(f(x) = ax^2; 0 < x < 4\)
- \(f(x) = kx^2 + kx + \frac 18; 0 < x < 8\)
- \(f(x) = kx; 0 < x < 4\)
- \(f(x) = 3x^2; 0 \le x \le 1\)
- \(f(y) = k(3y+5); 1 < y < 5\)
- \(f(z) = \frac29 (3z-z^2); 0 \le x \le 3\)
Problems Archive
Cumuluative Distribution Function
F(x) or cdf accumulates all of the probability less than or equal to.
| x | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P (x) | \(\frac 1 7\) | \(\frac 1 7\) | \(\frac 2 7\) | \(\frac 1 7\) | \(\frac 1 7\) | \(\frac 1 7\) |
| F (x) | \(\frac 1 7\) | \(\frac 2 7\) | \(\frac 4 7\) | \(\frac 5 7\) | \(\frac 6 7\) | \(1\) |
Find
- \(P(X<4)\)
- \(P(3<X<6)\)
cdf definition
\(F_X(x) = P(X\le x)\)
Discrete
\[F(x) = \sum_{X\le x} P(x)\]
Continuous
- \[F_{X}(x) = \int_{-\infty}^x f_X(t)dt\]
- Find cdf for \(f(x) = 2x; 0\le x \le 1\)
- \(\int \to x^2\)
\[\begin{eqnarray} F(x) = \begin{cases} x^2/2, & 0\le x \le 1 \\ 0, & \text{otherwise} \end{cases} \end{eqnarray}\]
cdf properties
- \(P(a\le x \le b) = F(b)-F(a)\)for \(a\lt b\); what if \(a \lt x \lt b?\)
- For continuous x, \(f(x) = \frac{d}{dx}[F(x)]\)
- \(F(-\infty) =0 , F(+\infty) = 1\)
Joint Probability Function
Let, \(I = Infected\), and \(V = Vaccinated\)
| \(I\) | \(\bar I\) | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| \(V\) | 3 | 276 | 279 |
| \(\bar V\) | 66 | 473 | 539 |
| Total | 69 | 749 | 818 |
Find the probability that
- a vaccinated person is infected
- a non-vaccinated person is uninfected
- These are joint probabilities \(\to\) P(x,y)
- \(P(x,y) =P(x) \cdot P(y)\) if \(x\) and \(y\) are independent.
Joint-Marginal-Conditional
Let, \(I = Infected\), and \(V = Vaccinated\)
| \(I\) | \(\bar I\) | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| \(V\) | 3 | 276 | 279 |
| \(\bar V\) | 66 | 473 | 539 |
| Total | 69 | 749 | 818 |
Find the probabilities that
- a vaccinated person is infected
- a non-vaccinated person is uninfected
- vaccinated if infected
- infected if not vaccinated
- vaccinated
- uninfected
Joint PF Properties
- \(P(x,y) \ge 0\)
- \(\Sigma\Sigma P(x,y)=1\)
Coin-Die
| Die/Coin | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H (1) | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H5 | H6 |
| T (0) | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 |
X = Outcome of coin toss
Y = Outcome of die throw
x = 0, 1; y = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
Construct the distribution.
Joint-Marginal-Conditional Revisited
| Exam (X) \(\to\) Result (Y) \(\downarrow\) |
PSC | JSC | SSC | HSC | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passed | 30 | 26 | 23 | 25 | 104 |
| Failed | 12 | 13 | 10 | 14 | 49 |
| Absent | 5 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 14 |
| Total | 47 | 41 | 36 | 43 | 167 |
- Marginal: \(P(Pass) = P(x_1)=P(x_1,y_1)+P(x_1,y_2)+P(x_1,y_3)\)
- \(P(Absent) = P(x_3) = P(x_3,y_1)+P(x_3,y_2)+P(x_3,y_3)\)
Marginal Probability
Consider the previous table
Joint probability: \(P(x_i, y_j); i = 1,2, \cdots m; j = 1,2, \cdots n\)
Marginal probability \(\to P(x_i) \leftarrow P(x_i, y_j)\)
- For x: \(P(x_i) = \sum_{j=1}^n P(x_i, y_j); i = 1,2, \cdots m\)
- For y: \(P(y_i) = \sum_{i=1}^m P(x_i, y_j); j = 1,2, \cdots n\)
- What about continuous x?
Marginal Probability Properties
- \(P(x_i) \ge 0\) and \(P(y_i) \ge 0\)
- \[\sum_{i=1}^m P(x_i)=\sum_{j=1}^n P(y_j)=1\]
Summing marginal probabilities will give 1.
Joint PMF Example
\(P(x,y) = \frac{x+y}{9}; x=0,1,2; y = 0, 1\)
- Find marginal probabilities
- Check properties (sum)
- \(P(x) = \frac{2x+1}{9}\)
Joint PDF Example
\(f(x,y) = \frac{2x+y}{3}; 0 \le x \le 1.5\) and \(0 \le y \le 1\)
Conditional Probability Function
Like Bayes Theorem
\(P(X_i|y_j) = \frac{P(x_i,y_j)}{P(y_j)}; P(y_j) \gt 0\)
Properties
- \(\sum_{j=1}^m P(x_i|y_j)=\sum_{i=1}^m P(y_j|x_i)=1\)
Conditional Probability Example
\(P(x,y) = \frac{x+y}{9}; x=0,1,2; y = 0, 1\)
Find \(P(X|Y)\) and \(P(Y|X)\)
Find for continuous X as well.
Find k for pdf
\(f(x) = kx^2+kx+\frac 1 8; 0 \lt x \lt 2\)
- Find k
- Find \(P(1 \lt X \lt 2)\)

docs.statmania.info | Abdullah Al Mahmud | Press space or arrow to change slides
 Source:
Source: